The modern web thrives on real-time interaction and instant data exchange. 🔄
Collaborative editing, live chat, and financial platforms demand bidirectional communication.
WebSocket protocol provides persistent, full-duplex channels over single TCP connections.
Unlike stateless HTTP, WebSockets maintain continuous, stateful links between clients and servers.
This stateful nature introduces unique troubleshooting challenges for developers.
Effective WebSocket debugging requires understanding the complete connection lifecycle.
This guide dissects common failures and provides persistence best practices.
The Handshake Nightmare: Initial Connection Failures 🤝
WebSocket connections begin with crucial handshake negotiations.
This one-time process upgrades HTTP connections to WebSocket protocol.
Failed handshakes prevent connections from ever opening properly.
The Upgrade Process 🔄
Clients initiate handshakes with specific upgrade headers in HTTP requests.
Servers must respond with 101 Switching Protocols status to complete upgrades.
Any response other than 101 indicates handshake failure requiring investigation.
Common Handshake Errors ❌
Handshake failures often appear as familiar HTTP errors with WebSocket context.
| HTTP Status Code | WebSocket Meaning | Troubleshooting Focus |
|---|---|---|
| 400 Bad Request | Malformed WebSocket headers | Client-side header formatting |
| 401 Unauthorized | Authentication failure | Server-side authentication logic |
| 403 Forbidden | Policy violation or permissions | CORS and authorization rules |
| 5xx Server Errors | Server exception during upgrade | Application server logs |
Network and Proxy Obstacles 🌐
Insidious handshake failures often stem from intermediary network components.
These devices may lack WebSocket protocol awareness causing connection issues.
- Firewalls and Proxies: May block connections or strip necessary upgrade headers. 🛡️
- Load Balancers: Require explicit WebSocket configuration and TCP routing. ⚖️
Use browser Developer Tools Network tab filtered by WS to inspect handshake headers.
The Mid-Life Crisis: Connection Drops and Data Errors 📉
Established connections face persistence challenges and data integrity issues.
Mid-connection failures often create silent disconnects without client awareness.
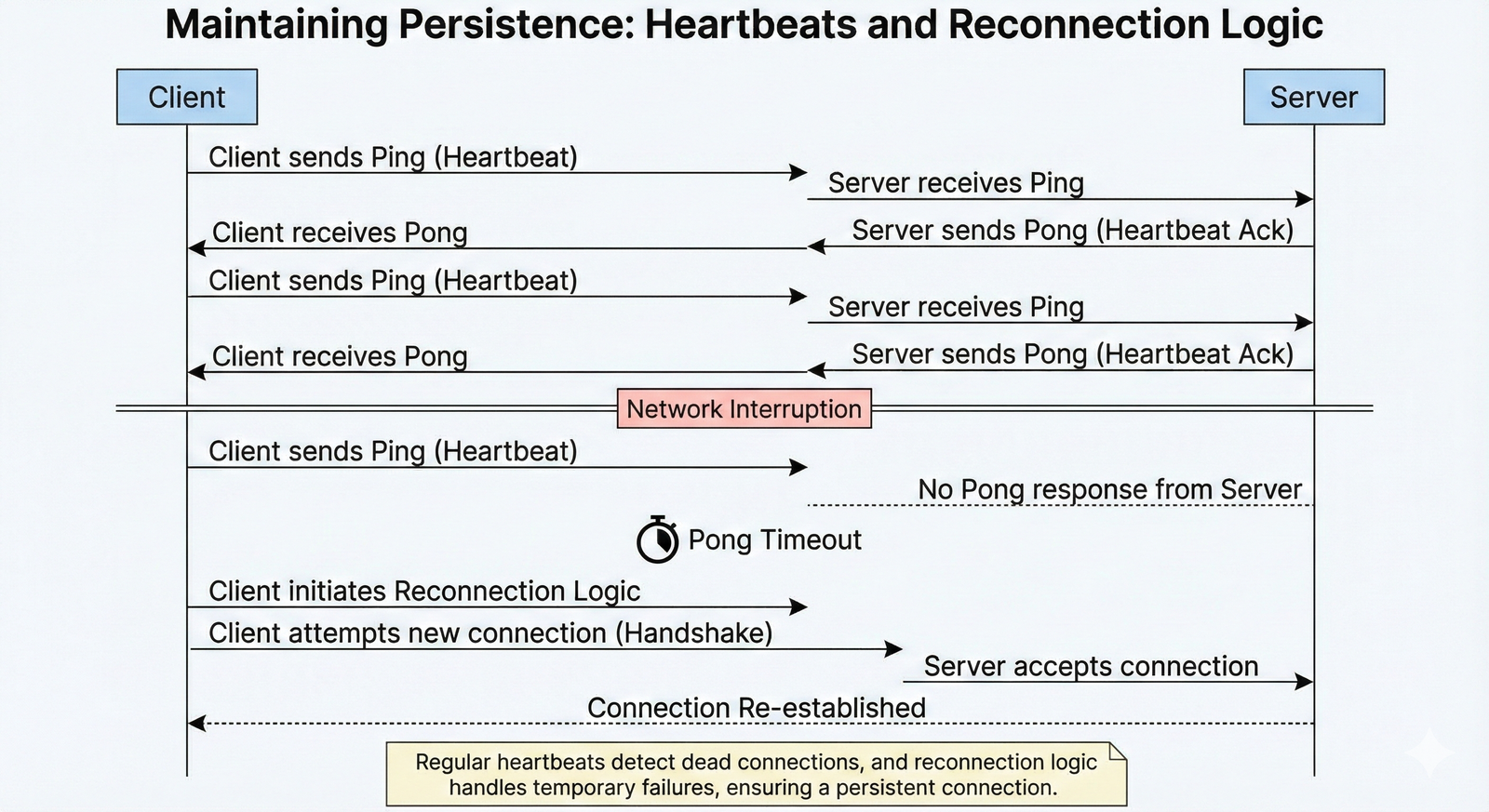
Silent Disconnects and Heartbeats 💓
Random connection drops frequently stem from intermediary idle timeouts.
Load balancers and proxies may close inactive connections after 60+ seconds.
Heartbeat mechanisms using Ping/Pong frames maintain connection activity.
- Server Pings: Send Ping frames regularly (every 30 seconds) to clients. 📤
- Client Pongs: Respond immediately with Pong frames to confirm liveness. 📥
This exchange resets idle timers and confirms end-to-end connection health.
Data Frame Errors 📦
WebSockets transmit data in text or binary frames with specific requirements.
Data-related errors typically involve encoding issues or size limitations.
- Encoding Errors: Non-UTF-8 data in text frames forces connection closure. 🔤
- Message Size Limits: Oversized messages trigger closure with specific codes. 📏
Implement strict server-side validation and logging for data frame issues.
Server-Side Resource Exhaustion 🚫
Stateful WebSocket connections consume significant server resources at scale.
Resource limitations can prevent new connections or cause sudden failures.
- File Descriptor Limits: Each connection consumes OS file descriptors. 📁
- Memory Constraints: Persistent connections require substantial memory allocation. 💾
Learn about WebSocket scalability strategies for high-traffic applications.
The End Game: Understanding WebSocket Close Codes 🔚
Close codes provide definitive explanations for connection terminations.
These 4-digit codes represent the most powerful WebSocket troubleshooting tool.
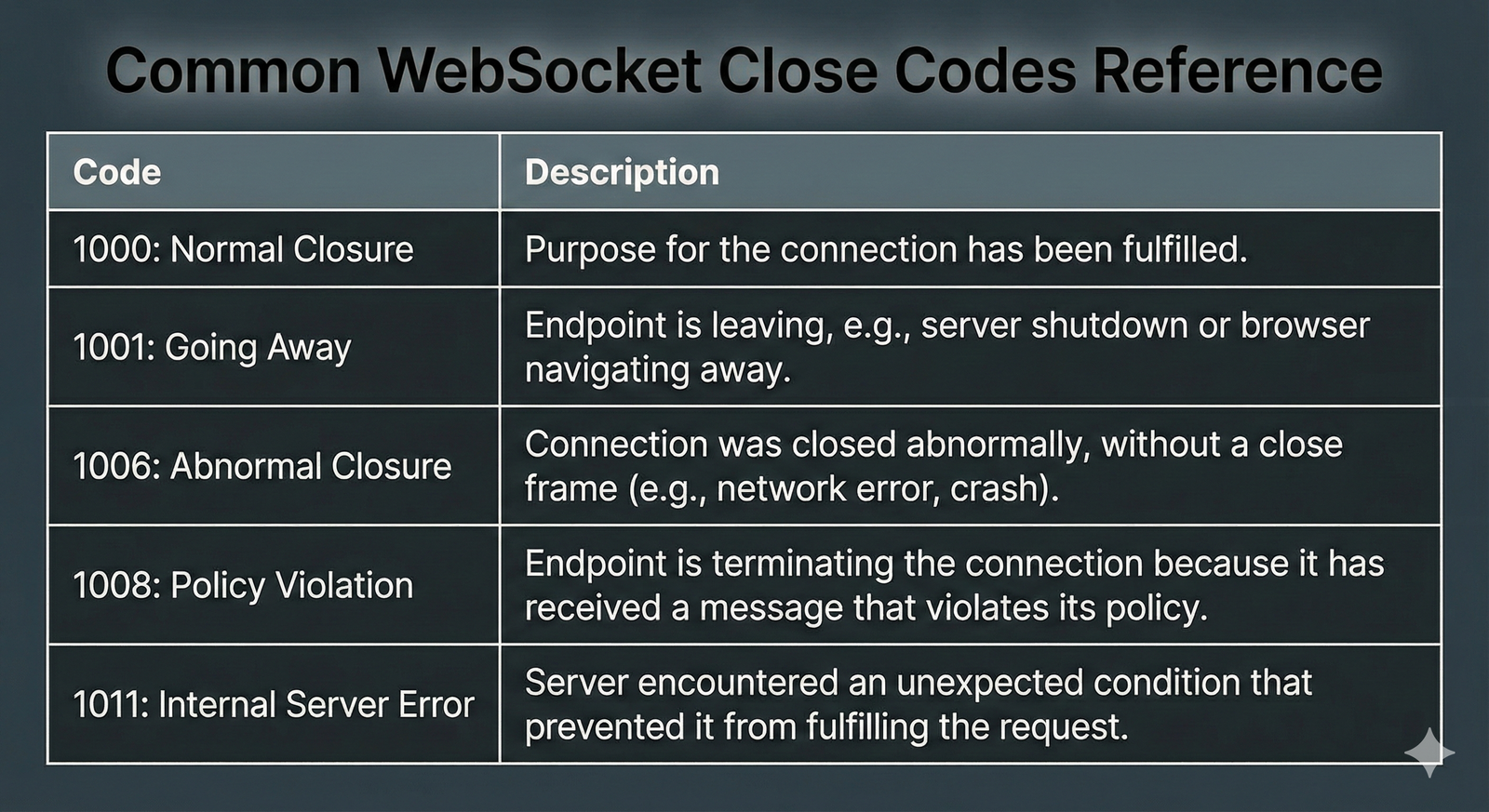
Key Standard Close Codes (1000-1015) 🔢
The WebSocket specification defines standard codes for common scenarios.
| Close Code | Name | Meaning and Context |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | Normal Closure | Graceful connection completion |
| 1001 | Going Away | Endpoint departure or shutdown |
| 1006 | Abnormal Closure | Network failure without close frame |
| 1008 | Policy Violation | Message violates server policy |
| 1009 | Message Too Big | Oversized message transmission |
1006 Abnormal Closure indicates network-level failures outside application control.
Custom Close Codes (4000-4999) 🎨
Custom codes enable application-specific error handling and intelligent reconnection.
These codes allow clients to react appropriately to server-initiated closures.
- 4001: Invalid Auth Token: Client can trigger immediate token refresh. 🔑
- 4002: Rate Limit Exceeded: Client can implement reconnection backoff. ⏱️
- 4003: Session Expired: Client can reauthenticate and establish new session. 🔄
Always log close codes and reason strings on both client and server for diagnosis.
Best Practices for Maintaining Persistence 🛡️
Robust real-time applications assume connection failures and design recovery accordingly.
Intelligent reconnection strategies transform fragile links into resilient channels.
Robust Reconnection Logic 🔄
Immediate reconnection attempts can overwhelm servers during outages.
Exponential Backoff with Jitter provides intelligent reconnection timing.
- Exponential Backoff: Wait exponentially longer between retries (1s, 2s, 4s…). 📈
- Jitter: Add random delays to prevent simultaneous client reconnections. 🎲
This approach gives servers recovery time and prevents cascading failures.
Session Recovery and State Management 💾
Stateful applications require session resumption beyond simple reconnection.
Clients must recover application state after reestablishing connections.
- Last Message ID: Clients send last received ID for server message replay. 📨
- Pub/Sub Architecture: Stateless servers with central message broadcasting. 🗣️
Explore real-time architecture patterns for scalable WebSocket implementations.
Conclusion: Mastering Real-Time Resilience 🏆
WebSockets form the backbone of modern real-time web applications.
Their stateful nature demands specialized troubleshooting beyond HTTP debugging.
Master connection lifecycles from handshakes through graceful closures.
Implement heartbeats to defeat idle timeouts and maintain persistent links.
Leverage close codes for definitive disconnection diagnosis and handling.
Intelligent reconnection logic transforms fragile connections into resilient communication channels.
WebSocket troubleshooting focuses on graceful failure handling rather than avoidance.
For more real-time insights, explore our WebSocket best practices and MDN WebSocket documentation.
