A L👀K
The journey of circuits began with early explorations into static electricity 🔌
where pioneers of the field sought to understand the mysterious forces that could produce sparks and light.
The phenomenon inspired scientific inquiry, leading to significant breakthroughs.
One of the pivotal milestones in this evolution was the invention of the battery by Alessandro Volta in 1800,
which provided a stable source of electric current.
This invention was crucial as it allowed for controlled experiments and paved the way for further developments in electrical technology.
As the understanding of electrical principles advanced, Ohm’s Law emerged in the 1820s, formulated by the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm.
This fundamental law established a relationship between voltage, current, and resistance,
providing a critical framework for analyzing electrical circuits.
With this foundation, engineers and scientists began to create more complex and practical applications of electricity,
leading to inventions that transformed daily life.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, significant figures such as Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla made groundbreaking contributions to the world of circuits.

Edison’s development of the practical light bulb and the electrical power distribution system helped to usher in the age of electricity,
bringing illumination to households and industries alike.
Tesla, known for his work on alternating current (AC) systems, revolutionized electrical energy transmission,
allowing electricity to be efficiently delivered over long distances.
Further advancements were made in the latter half of the 20th century,
notably with the invention of the integrated circuit by Jack Kilby in 1958.
This innovation marked a leap in technology, as multiple electronic components could now be integrated into a single device,
significantly reducing size and improving efficiency.
As circuit technology evolved, it laid the foundation for the digital age we live in today.
Analog to Digital
The transition from analog to digital circuits marks a significant milestone in the evolution of technology.
Historically, analog circuits were predominant, relying on continuously variable signals to represent information.
However, the advent of digital technology has radically transformed how these signals are processed, stored, and transmitted.
Digital circuits utilize discrete signals for signaling, offering enhanced precision,
noise resistance, and improved scalability,
establishing them as a superior choice for modern applications.
With the development of nanotechnology, the size of electronic components has shrunk dramatically, leading to
smaller
faster
more efficient circuits.
This miniaturization has facilitated the creation of flexible circuits, allowing for the integration of electronics into a variety of unconventional surfaces and materials.
These flexible circuits have opened new avenues for applications in wearable technology, smart textiles,
and even biomedical devices.
Their adaptability is particularly relevant in the rapidly growing field of the Internet of Things (IoT),
where connectivity and efficiency are paramount.
Moreover, the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation has influenced circuit design significantly.
Machine learning algorithms are now used to optimize circuit layouts and enhance performance, reducing human error and speeding up the design process.
Automation in manufacturing has also streamlined production, resulting in standardized, high-quality circuit components.
This synergy between AI and circuit technology is reshaping industries, enabling smarter devices capable of performing complex tasks autonomously.
As such, the shift from analog to digital circuits, combined with the advancements in nanotechnology,
flexible circuit design, and AI implementation, continues to propel technological innovation.
These developments not only enhance the capabilities of circuits but also pave the way for ground-breaking applications that could redefine consumer electronics and overall connectivity in the modern world.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting electrical circuits is a critical skill for anyone working with electronics, whether a novice or a seasoned professional.
Understanding common issues, such as short circuits, broken connections, and overheating helps in efficiently diagnosing and rectifying problems.
A short circuit occurs when electricity flows along an unintended path, often resulting in system failure.
In contrast, broken connections can lead to incomplete circuits, causing devices not to operate at all.
Overheating typically indicates excessive current flow or component failure, necessitating immediate attention.
One of the primary tools in troubleshooting is the multimeter.
This versatile device can measure voltage, current, and resistance, enabling users to pinpoint discrepancies in circuits.
A multimeter can quickly determine if power is reaching various components,
thus identifying potential short circuits or broken connections.
Additionally, thermal cameras can be invaluable in detecting overheating components by visualizing hot spots that could pose hazards or signal malfunctioning parts.
By recognizing these signs early, users can prevent further damage to their circuits.
Safety should never be overlooked when working with electrical circuits.
Always ensure devices are powered down and disconnected from their power sources before beginning any troubleshooting process.
Employing personal protective equipment, such as insulated gloves and safety goggles,
can further enhance safety while dealing with potentially hazardous components.
Maintaining a well-organized workspace and systematically addressing circuit problems can help streamline the troubleshooting process.
By familiarizing oneself with these troubleshooting basics, as well as the appropriate tools and safety practices,
beginners can cultivate their confidence in handling electrical systems.
This foundational knowledge serves as a stepping stone for deeper explorations into electronics,
empowering individuals to solve common circuit issues in their projects effectively.
Fun Facts
The journey of circuits from their humble beginnings to their modern configurations is fraught with fascinating developments and milestones.
One of the most striking aspects of this evolution is the transformation in size and capability.
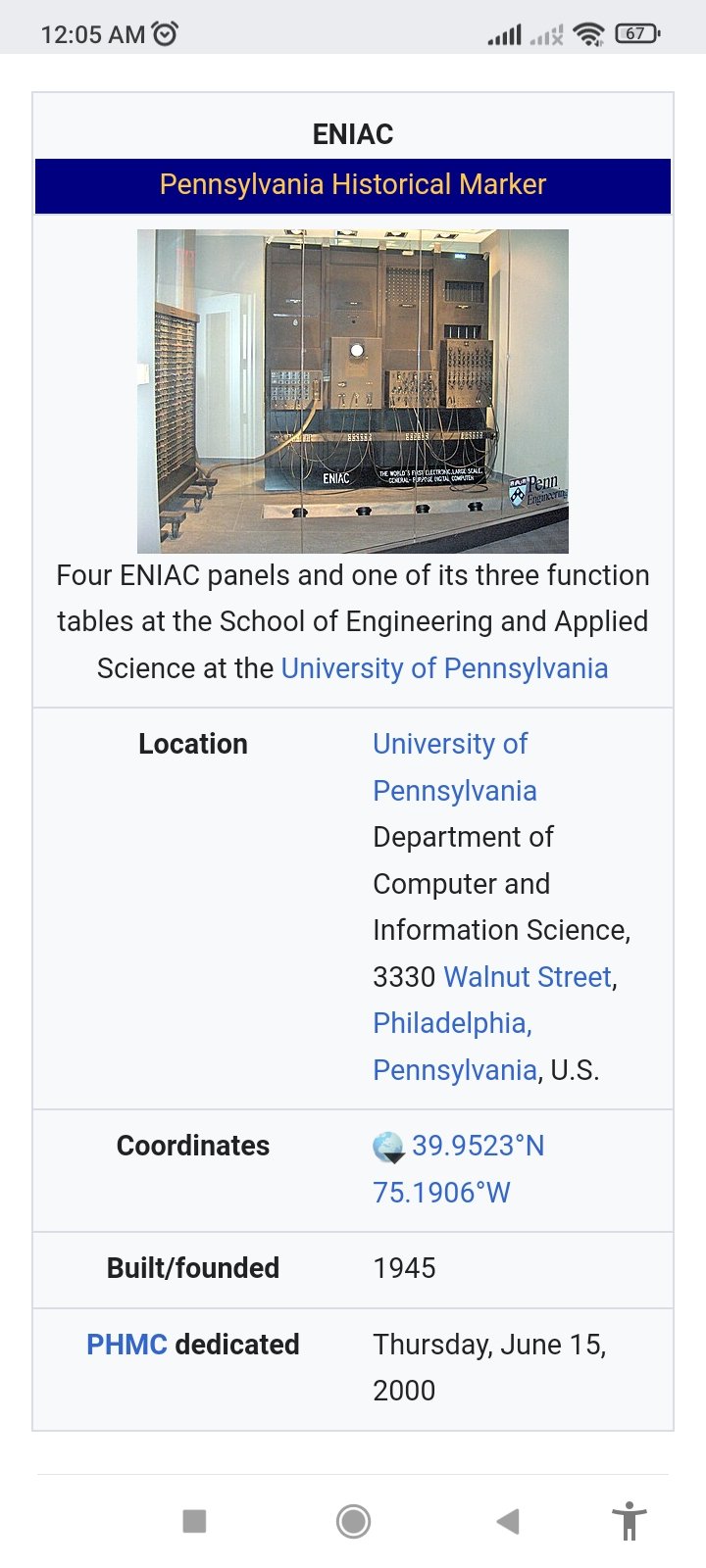
The first computer circuit, which was part of the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) developed in the 1940s,
occupied an entire room and weighed over 27 tons.
May be looking like this as we tried with ai generator

Not really 😞 😞
In stark contrast, today’s sophisticated circuits fit into microchips that are often smaller than a fingernail yet possess exponentially greater processing power and efficiency.
Simply amazing 😍
This dramatic technological leap underscores how far circuit design and fabrication have progressed.
Circuits are not only foundational to computing; they enable a plethora of real-world applications across diverse fields.
In telecommunications, microcircuits are integral to smartphones,
allowing for rapid communication and data transfer across the globe.
Simultaneously, innovations in medical devices like pacemakers and MRI machines highlight the role of circuits in enhancing healthcare.
Similarly, the development of electric vehicles relies heavily on advanced circuit technology to improve efficiency and performance,
particularly in battery management systems.
These applications demonstrate the vital role that circuits play in everyday life.
Looking to the future, the field of circuits is ripe with exciting prospects.
Emerging trends such as quantum computing promise to revolutionize processing speeds and capabilities beyond what classical circuits can achieve.
Additionally, research into biodegradable circuits is paving the way for environmentally friendly electronics that minimize waste and reduce their ecological footprint.
These innovations not only reflect the ingenuity and adaptability of circuit design but also foreshadow a world where technology and sustainability work hand in hand.
The evolution of circuits is ongoing, consistently bringing forth new possibilities and transforming our world.
Analogies
To comprehend the intricate world of circuits, one might find it helpful to visualize them as highways designed specifically for electrons.
Just as cars travel along roads, electrons navigate through pathways in a circuit to reach their destination,
which ultimately translates to powering devices in our daily lives.
This analogy not only simplifies the concept but also aids in grasping the complexities of electrical flow, resistance, and connectivity.
Consider how congested traffic can impede movement; similarly,
a high resistance in a circuit restricts electron flow, affecting the efficiency of electrical devices.
Moreover, by personifying the components of a circuit, one can envision resistors as roadblocks,
capacitors as storage units for energy, and transistors as traffic lights that regulate flow.
These engaging analogies not only make the learning process enjoyable but also create a deeper understanding of how circuits function.
As you explore these concepts, it is essential to consider how they relate to the technologies and electronics you interact with daily.
For instance, every time you switch on a light or charge your phone,
you are witnessing the seamless operation of a circuit.
To foster engagement further, we encourage readers to partake in DIY projects that involve basic circuit creation.
Whether it is constructing a simple LED circuit with a battery, or experimenting with a breadboard setup,
these hands-on experiences can significantly enhance your grasp of circuits.
Additionally, we invite you to share your experiences with electronic devices or any fascinating projects you have undertaken.
Building a community centered around circuit learning and experimentation not only enriches individual knowledge but also promotes collaborative discovery,
enhancing the overall experience of exploring the evolution of circuits.
Role
Circuits form the backbone of modern technology, making them indispensable in our daily lives.
From the moment we wake up to the sound of an alarm clock to the time we wind down with an evening show, circuits are at work,
ensuring that our household appliances function seamlessly. Basic devices such as toasters, refrigerators,
and microwaves rely on electrical circuits to operate efficiently.
These circuits enable the transfer of electricity that drives these appliances, providing the convenience we often take for granted.
Moreover, circuits play a fundamental role in communication technologies.
Telecommunication networks, which comprise various devices such as phones and routers, rely heavily on circuits to transmit and receive information.
This includes everything from a simple phone call to high-speed internet connectivity.
By utilizing circuit technology, communication becomes instantaneous, allowing us to connect with others around the globe effortlessly.
The integration of smart technology into our homes underscores the importance of circuits even further.
Smart homes, equipped with connected devices, utilize intricate circuit designs to facilitate automation and remote control.
For instance, energy-efficient lighting systems adjust based on occupancy,
while security systems can be monitored from anywhere in the world.
These circuits transform our living spaces into efficient, user-friendly environments that enhance our overall quality of life.
Additionally, the advancement of circuit technology paves the way for innovation in various sectors, including healthcare, entertainment, and transportation.
In healthcare, for instance, medical devices such as heart monitors and MRI machines depend on complex circuits to function properly, thus improving patient outcomes.
The ability to harness circuits for diverse applications highlights their critical role in shaping our everyday experiences.
Profiles
The evolution of circuits has been significantly shaped by remarkable individuals whose contributions have paved the way for modern technology.
Among these pioneers, Thomas Edison stands out for his innovation in electric power systems.
Born in 1847, Edison became a prolific inventor, with numerous patents to his name, including the electric light bulb and the phonograph.
He established the first investor-owned electric utility, the Edison Electric Light Company, which helped lay the foundation for widespread electrical distribution.
Edison’s work not only expanded the use of electricity but also emphasized the importance of circuit design in ensuring safety and efficiency in power systems.
Another pivotal figure is Nikola Tesla, a contemporary of Edison, known for his groundbreaking work in electromagnetism.
Tesla, born in 1856, conceptualized alternating current (AC) electrical systems, which revolutionized power transmission.
His inventions, such as the Tesla coil and induction motor, showcased the potential of circuits operating on AC,
facilitating the development of long-distance electricity distribution.
Tesla’s vision of wireless energy transfer and his numerous innovations laid the groundwork for future technological advancements,
making his contributions critical in the field of circuitry.
While Edison and Tesla are often highlighted, other lesser-known figures have also made significant impacts.
Jack Kilby, an American engineer, is credited with inventing the integrated circuit, a crucial development that led to the miniaturization of electronic devices.
His creation in 1958 revolutionized technology by allowing multiple components, such as resistors and capacitors, to be fabricated onto a single semiconductor material.
This invention set the stage for the proliferation of consumer electronics and complex digital systems that we rely on today.
Understanding the personal stories and innovations of these pioneers fosters a deeper appreciation for the advancements in circuitry that define modern technology.
Innovative
The evolution of circuit design and engineering has given rise to numerous innovative technologies that significantly impact modern society.
At the forefront are integrated circuits (ICs), which are pivotal in revolutionizing electronic devices.
An integrated circuit combines multiple components, such as transistors and resistors, into a single chip,
which greatly reduces the size and cost of electronic systems while enhancing performance and reliability.
This technology has enabled the miniaturization of devices,
allowing for the development of compact electronics that we rely on today, from smartphones to medical devices.
Another groundbreaking innovation stemming from circuit advancements is the microprocessor.
The microprocessor functions as the brain of a computer,
processing instructions and managing data flow.
Its introduction marked a significant milestone in computing,
leading to the creation of personal computers,
advanced gaming consoles, and sophisticated computing systems used in various industries.
As microprocessors have evolved, they have become more powerful, energy-efficient, and capable of performing complex tasks,
which has further integrated technology into our daily lives.
Additionally, the advancements in circuit technology have propelled the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT).
IoT devices are embedded with sensors and interconnected through the internet, allowing for seamless communication and data exchange.
The development of smaller, efficient circuits facilitates the creation of smart home devices, wearable technology, and industrial automation systems.
This advancement not only enhances convenience and efficiency but also paves the way for innovative applications across various sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and transportation.
In summary, the continuous innovations in circuit technology, such as integrated circuits and microprocessors, are vital in shaping the technological landscape.
These developments have significantly enhanced the functionality, efficiency, and integration of electronics,
ultimately transforming how we interact with the world around us.
Future
As we delve into the future of circuit technology, it is essential to recognize the rapid advancements that have taken place over the past few decades.
Emerging technologies such as quantum circuits are poised to revolutionize the way we think about and utilize circuitry.
Unlike traditional circuits, quantum circuits leverage the principles of quantum mechanics, allowing for unprecedented computational capabilities.
These circuits hold the potential to solve problems that are currently intractable for classical computers,
making them a focal point for researchers and developers alike.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence in circuit design is another trend that promises to reshape the landscape of circuit technology.
AI-driven tools can optimize circuit layouts and enhance performances while minimizing size and power consumption.
This synergy between AI and traditional circuitry provides a pathway to smarter,
more efficient electronic devices that can adapt to user needs in real-time.
An important development to consider is the growing trend toward sustainable and biodegradable materials in circuit manufacturing.
As concerns about electronic waste continue to mount, researchers are actively exploring alternatives that reduce environmental impact.
Innovations such as organic electronics and materials derived from natural sources suggest a future where circuits are not only functional but also eco-friendly.
This shift towards sustainability in circuit technology not only meets the needs of a conscientious consumer base but also aligns with global efforts to combat climate change.
The continuous evolution of circuits underscores the significance of innovation and adaptability in an increasingly connected world.
By embracing emerging technologies and sustainable practices,
the future of circuits is likely to be characterized by enhanced performance, eco-friendliness, and versatility.
Such advancements invite curiosity and stimulate a mindset of continuous learning,
paving the way for novel applications and solutions that we have yet to envision.
Let me know about your thoughts 💭 💭.