
The year is 2025, and you are staring at a spinning wheel.
It is the digital equivalent of a traffic jam on a deserted highway, a frustrating, soul-crushing symbol of a promise broken: the promise of instant connectivity.
Your internet, once a sleek, high-speed bullet train, has devolved into a sputtering, coal-powered locomotive, and you are the only passenger.
But fear not, for today, you are not just a user; you are a Digital Detective, armed with the knowledge to unmask the hidden culprits and restore your connection to its rightful warp speed.
This is your comprehensive, creative, and slightly dramatic guide to slow internet troubleshooting.

Phase I: The Baseline Investigation (Establishing the Crime Scene)
Before you can fix a problem, you must first prove that a problem exists and measure its severity.
The first tool in your detective kit is the Speed Test [1].
Think of your internet plan as a contract promising a certain amount of water flow—say, 300 megabits per second (Mbps).
A speed test is the digital equivalent of measuring the water pressure coming out of your tap.
Run a test on a reliable site like Ookla or Google’s speed test, and make sure to do it on a device connected directly to your router via an Ethernet cable, if possible, to eliminate Wi-Fi interference.
The results will give you three crucial numbers: Download Speed, Upload Speed, and Latency (Ping).
If these numbers are significantly lower than what your Internet Service Provider (ISP) promised, you have a case.
Phase II: The Golden Rule of Connectivity (The First Suspect)
Every detective knows that the simplest explanation is often the correct one.
In the world of networking, this is the Reboot.
Your modem and router are like two overworked civil servants who haven’t had a coffee break in months.
They accumulate temporary data, memory leaks, and conflicting instructions until they simply slow down from exhaustion [2].
The solution is simple, yet profoundly effective:
- Unplug both the modem and the router from the power source.
- Wait a full 60 seconds. This is crucial; it ensures all residual power is drained and the memory is completely cleared.
- Plug the modem back in first. Wait until all its lights are solid and stable (usually 2-5 minutes).
- Plug the router back in second. Wait another 2-3 minutes for it to boot up and establish a connection with the modem.
This simple act resolves a surprising majority of slow internet complaints.
Phase III: The Wi-Fi Whisperer (The Invisible Obstacles)
If the reboot failed, the next suspect is your Wi-Fi signal—the invisible messenger carrying your data.
Wi-Fi is susceptible to interference and physical barriers.
Imagine your Wi-Fi signal as a voice trying to shout across a crowded room; the further away you are, and the more walls are in the way, the harder it is to hear.
The key here is Router Placement [3].
Your router should be:
- Central: In the middle of your home, not tucked away in a corner.
- High Up: On a shelf or table, as signals tend to broadcast downward.
- Away from Obstacles: Especially metal objects, fish tanks (water is a signal killer), and other electronics like microwaves or cordless phones.
Furthermore, check your Frequency Band.
Most modern routers offer two bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
The 2.4 GHz band travels further and penetrates walls better, but it is slower and more prone to interference from other devices.
The 5 GHz band is much faster but has a shorter range.
For devices close to the router (like your main PC or streaming box), switch to the 5 GHz band for maximum speed.
Phase IV: The Bandwidth Bandits (The Hidden Hogs)
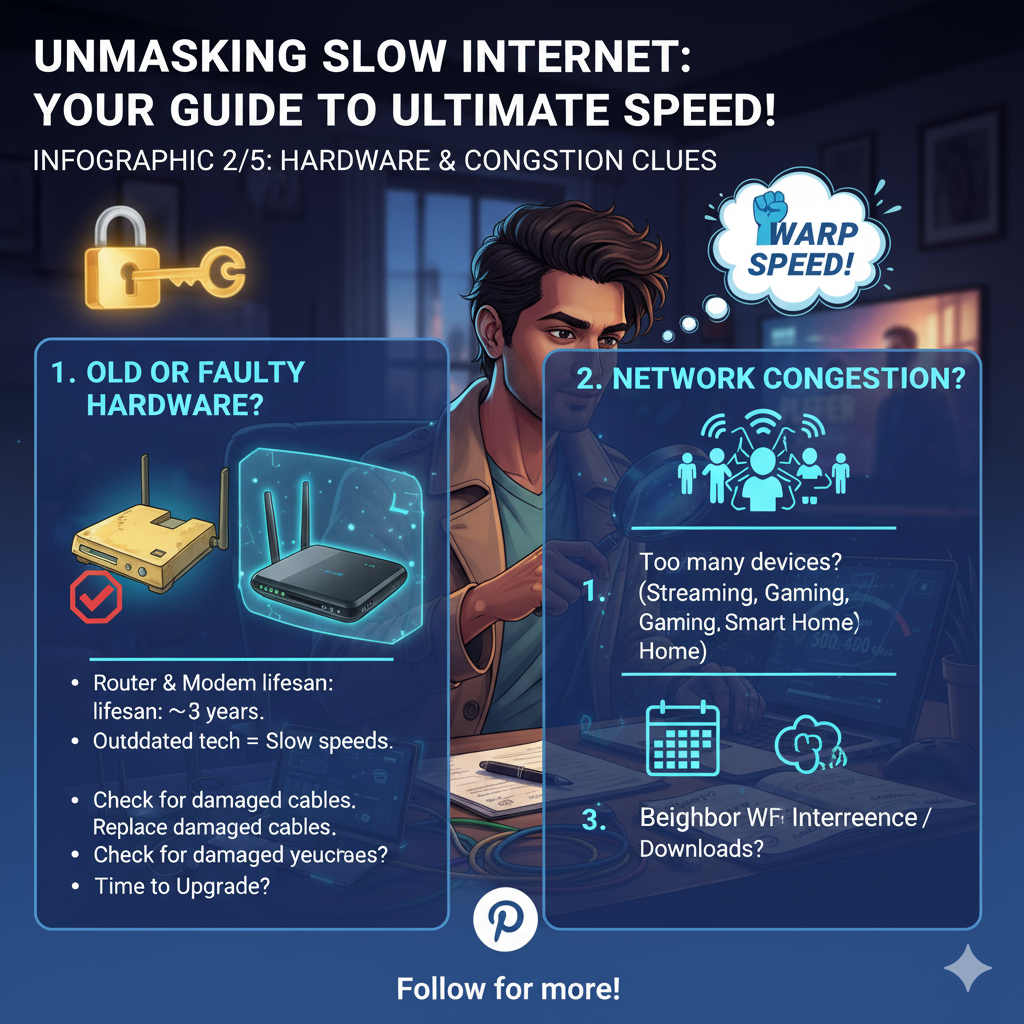
Sometimes, your internet is not slow; it is simply overloaded.
This is the work of the Bandwidth Bandits—devices or applications secretly consuming your precious data allowance.
Think of your bandwidth as a single garden hose; if you connect ten sprinklers to it, each one will only get a trickle.
The culprits often include:
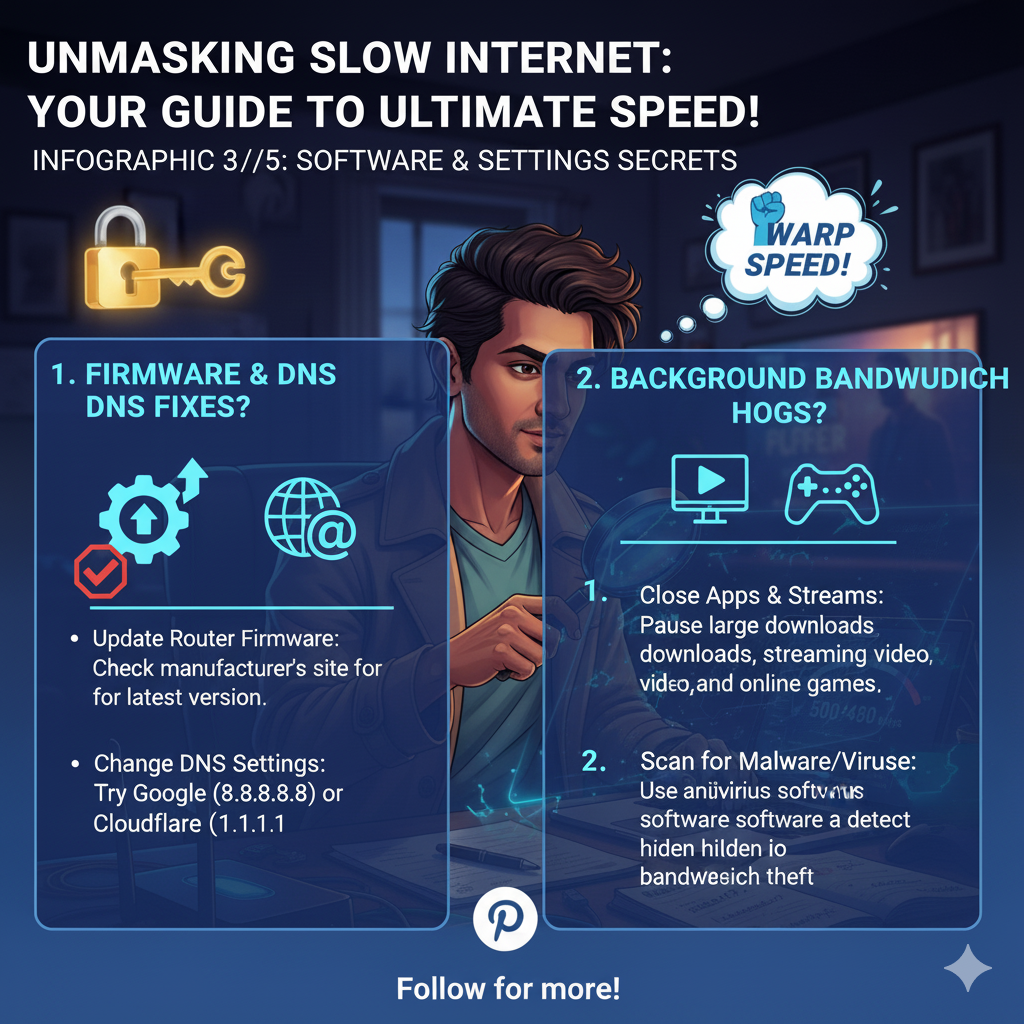
- Background Downloads/Updates: Steam, Epic Games, Windows, or macOS updates often run in the background without notification.
- Cloud Syncing: Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive constantly upload and download files.
- Too Many Streaming Devices: Multiple 4K streams (Netflix, Disney+, etc.) can quickly saturate a standard connection.
Actionable Step: Temporarily disconnect all devices except the one you are testing.
If the speed dramatically improves, you have identified the problem as Network Congestion [4].
You can manage this by using your router’s Quality of Service (QoS) settings, which allow you to prioritize traffic for certain applications (like video conferencing) over others (like large downloads).
Phase V: The Aging Arsenal (Outdated Equipment)
Technology ages, and your networking gear is no exception.
An old router or modem can be the bottleneck in your entire system, regardless of how fast your ISP’s connection is.
If your router is more than five years old, it likely lacks support for modern standards like Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) or even Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac).
It is like trying to put a Formula 1 engine into a 1980s chassis; the chassis simply cannot handle the power.
Check Your Firmware: Even if your equipment is relatively new, outdated firmware can cause performance issues and security vulnerabilities.
Log into your router’s administrative interface (usually by typing 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1 into your browser) and look for a firmware update option.

This is a critical maintenance step that many users overlook.
Phase VI: The Digital Parasites (Malware and Spyware)
Sometimes, the slowdown is not external but internal, caused by digital parasites lurking on your computer.
Malware and Spyware can silently run in the background, consuming system resources and, more importantly, using your internet connection to send data to remote servers [5].
This constant, unauthorized data transfer can severely degrade your connection speed.
Actionable Step: Run a full system scan using a reputable antivirus and anti-malware program.
If your computer is infected, removing the parasite will often result in an immediate and noticeable speed increase.
Phase VII: The Final Confrontation (Calling the ISP)
If you have diligently completed all the steps above—rebooted, optimized Wi-Fi, checked for congestion, updated firmware, and scanned for malware—and your speed test results are still abysmal, it is time for the final confrontation.
The problem is likely outside your home, residing with your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Before you call, ensure you have the following evidence:
- Your Speed Test Results: Specifically, the low numbers you recorded while connected directly to the modem.
- Your Troubleshooting Log: Mention that you have already rebooted the modem and router, checked for network congestion, and verified your equipment.
This preparation is key; it prevents the ISP representative from simply telling you to “turn it off and on again.”
They can then check for line noise, area outages, or provisioning issues on their end, which are problems only they can resolve.
The Digital Detective’s Summary Checklist
Keep this checklist handy for the next time the spinning wheel of doom appears.
| Step | Action | Culprit Targeted |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Baseline | Run a speed test (wired connection preferred). | Verify the problem is real. |
| 2. Reboot | Power cycle modem, then router (wait 60 seconds). | Temporary glitches, memory leaks. |
| 3. Wi-Fi Check | Optimize router placement; switch to 5 GHz band. | Signal interference, physical barriers. |
| 4. Congestion | Disconnect all other devices; check background apps. | Bandwidth-hogging devices/apps. |
| 5. Equipment | Update router firmware; consider replacing old hardware. | Outdated technology, software bugs. |
| 6. Scan | Run a full system scan for malware and spyware. | Digital parasites consuming bandwidth. |
| 7. Call ISP | Contact provider with speed test evidence. | External line issues, area outages, provisioning errors. |
The internet is the backbone of modern life, and a slow connection is more than an inconvenience—it is a barrier to productivity and entertainment.
By following these steps, you transition from a frustrated victim to a proactive Digital Detective, capable of diagnosing and solving the mystery of the missing speed.
Go forth and conquer the buffering!
References
[1] Ookla. (2022). How to Fix Your Family’s Slow Internet: A Basic Troubleshooting Guide. https://www.ookla.com/articles/fix-your-familys-slow-internet
[2] HighSpeedInternet.com. (2025). 8 Reasons Why Your Internet is Slow (and How to Fix It). https://www.highspeedinternet.com/resources/why-is-my-internet-so-slow
[3] Norton. (2025). Why is my internet so slow? 11 causes + how to speed it up. https://us.norton.com/blog/wifi/why-is-my-internet-so-slow
[4] REV. (2025). How To Fix Slow Internet Speeds at Home. https://letsrev.com/how-to-fix-slow-internet/
[5] CenturyLink. Troubleshoot Slow Internet. https://www.centurylink.com/home/help/internet/troubleshoot-slow-internet.html
