The world of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is expanding at an astonishing pace. 🚀
From intelligent home assistants to complex industrial robots, AI is weaving itself into every aspect of our lives. 💡
At the heart of this revolution lies the crucial concept of AI integration. 🧠
It’s not enough to simply have powerful AI algorithms; these algorithms must interact seamlessly with the physical world. 🌍
This interaction is largely facilitated by advanced peripherals. 🔌
Without compatible and well-integrated peripherals, even the most sophisticated AI remains confined to the digital realm. 💻
This blog post dives deep into the “AI Integration Imperative,” focusing specifically on advanced peripheral compatibility and troubleshooting. 🛠️
We’ll explore why this is so vital, the challenges involved, and practical strategies to ensure smooth operation. 🌟
Why Peripheral Compatibility is Paramount in AI
Think of an AI system as a brain. 🧠
Peripherals are its senses and limbs. 👀👂✋
Just as a human brain relies on eyes to see and hands to interact, an AI needs cameras, sensors, microphones, and actuators to perceive and act upon its environment. 🌐
When these peripherals aren’t compatible, the AI system becomes hobbled, much like a person with impaired senses. 🤕
For AI, incompatibility can manifest in several ways. 📉
It might be a simple driver conflict, leading to a device not being recognized. 🤷♀️
Or it could be a more complex issue, where data formats don’t match, causing garbled input or incorrect outputs. 😵
In critical AI applications, such as autonomous vehicles or medical diagnostic tools, even minor compatibility issues can have catastrophic consequences. 🚨
Imagine an autonomous car’s LIDAR sensor suddenly becoming incompatible with the central AI – the results could be devastating. 💥
Therefore, ensuring robust peripheral compatibility is not just a technical detail; it’s a fundamental requirement for the reliable and safe operation of AI systems. ✅
“The first rule of any technology used in a business is that automation applied to an efficient operation will magnify the efficiency. The second is that automation applied to an inefficient operation will magnify the inefficiency.” – Bill Gates
The Ecosystem of Advanced AI Peripherals
The term “peripheral” in AI extends far beyond traditional keyboards and mice. ⌨️🖱️
It encompasses a diverse range of specialized hardware designed to provide AI with rich data streams and sophisticated control capabilities. 🎯
Let’s look at some key categories: 👇
Sensors: The AI’s Eyes and Ears 👁️👂
These include high-resolution cameras for computer vision, LiDAR sensors for 3D mapping, radar for object detection in adverse weather, microphones for natural language processing, and various environmental sensors (temperature, humidity, pressure) for contextual awareness. 🌡️
Each sensor generates unique data types and requires specific drivers and communication protocols. 📡
Actuators: The AI’s Hands and Feet 🦵🖐️
These are the devices that allow AI to interact with the physical world. 🌎
Examples include robotic arms, motors, grippers, and display devices. 🤖
Actuators often require precise control signals and feedback loops, making compatibility with AI control software paramount. 🚦
Edge AI Devices: Local Intelligence 🧠
These are specialized hardware units, often with their own processors, designed to run AI models directly at the data source (on the “edge” of the network). 📶
This includes AI-powered security cameras, smart manufacturing sensors, and embedded systems in IoT devices. 🏡
Compatibility here means ensuring the edge device can effectively communicate with both the central AI platform and other local peripherals. 🔗
The challenge lies in ensuring all these disparate components can speak the same language and work in harmony. 🎶
Common Compatibility Challenges 😥
Integrating advanced peripherals with AI systems is rarely a plug-and-play experience. 🔌❌
Several common hurdles often arise: 🚧
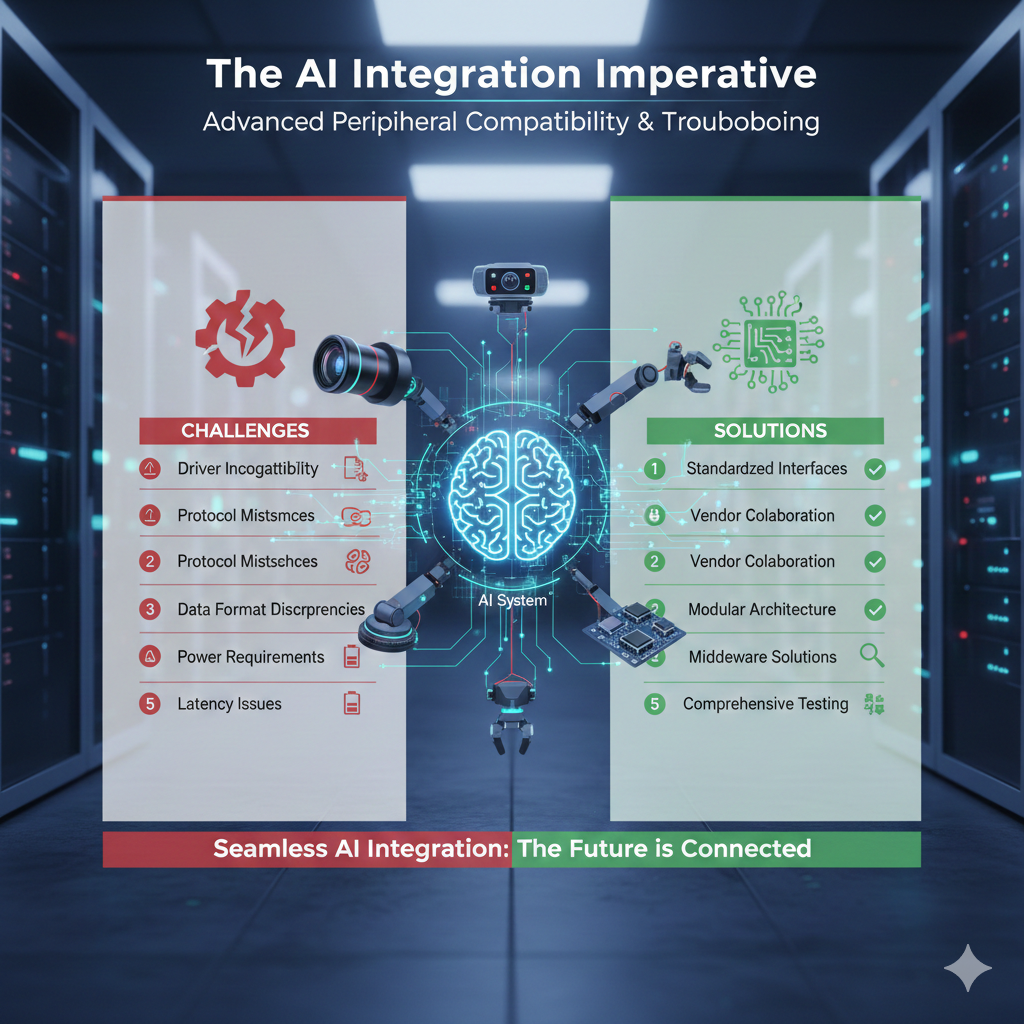
- Driver Incompatibility: One of the most frequent issues. An outdated, incorrect, or missing driver can render a peripheral useless, preventing the AI system from recognizing or properly communicating with it. 💾
- Protocol Mismatches: Different peripherals might use different communication protocols (e.g., USB, Ethernet, proprietary serial protocols). The AI system needs to be able to understand and transmit data using the correct protocol for each device. 📡
- Data Format Discrepancies: Sensors output data in various formats (e.g., raw pixel data, JSON, CSV). The AI’s input pipeline must be configured to correctly parse and interpret this data. 📊
- Power Requirements: Advanced peripherals, especially those with high-performance sensors or actuators, can have significant power demands. Insufficient power supply can lead to erratic behavior or complete failure. ⚡
- Latency Issues: For real-time AI applications (e.g., robotics, autonomous systems), data transfer latency is critical. Incompatible hardware or inefficient software can introduce delays that compromise performance. 🐌
- Firmware Differences: Peripherals often have their own internal firmware. Incompatibility between firmware versions and the AI’s operating system or control software can lead to unexpected issues. 🔄

- Security Vulnerabilities: Each connected peripheral represents a potential entry point for security breaches. Ensuring compatibility also means ensuring secure communication and data handling. 🔒
Strategies for Ensuring Seamless Compatibility 💪
Proactive planning and careful execution are key to overcoming compatibility challenges. 🔑
Here are some effective strategies: 👇
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Standardized Interfaces | Prioritize peripherals that adhere to industry standards (e.g., USB-C, Ethernet/IP, ROS). This significantly reduces compatibility headaches and simplifies integration. |
| Vendor Collaboration | Work closely with peripheral vendors. Many offer dedicated SDKs, APIs, and technical support to ensure their devices integrate well with AI platforms. |
| Modular Architecture | Design AI systems with a modular approach. This allows for easier swapping of peripherals and isolation of compatibility issues, making troubleshooting more efficient. |
| Middleware Solutions | Utilize middleware (e.g., ROS, MQTT brokers) to abstract away hardware-specific details. This provides a unified interface for the AI system, regardless of the underlying peripheral. |
| Comprehensive Testing | Thoroughly test all peripherals in the target AI environment before full deployment. Simulate various operating conditions to identify potential issues early. |
Regular software updates are also crucial, as they often include bug fixes and improved driver support for peripherals. 🔄
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques for AI Peripherals 🧐
Even with the best planning, problems can arise. 😔
Effective troubleshooting is a critical skill for anyone working with AI integration. 🛠️
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process 🔍
- Isolate the Problem: Determine if the issue is with a specific peripheral, the AI software, or the communication channel. Try disconnecting other peripherals to narrow down the cause. ✂️
- Check Physical Connections: A surprisingly common cause of issues. Ensure all cables are securely plugged in, undamaged, and connected to the correct ports. 🔌✅
- Verify Power Supply: Confirm the peripheral is receiving adequate power. Check power indicators on the device and measure voltage if necessary. 💡
- Driver and Firmware Check: Ensure the latest and correct drivers are installed. Check for any available firmware updates for the peripheral. 💾
- Monitor System Logs: Operating system logs, AI framework logs, and device-specific logs often contain valuable error messages and warnings that can pinpoint the problem. 📝
- Network Diagnostics: For network-connected peripherals, use tools like
ping,traceroute, or network sniffers to diagnose connectivity and latency issues. 🌐 - Test with Known Good Components: If possible, swap out the problematic peripheral with a known working unit to determine if the issue is with the device itself or the system it’s connected to. 🔄
“Innovation distinguishes between a leader and a follower.” – Steve Jobs
Leveraging AI for Troubleshooting 🤖💡
Ironically, AI itself can be a powerful tool for troubleshooting peripheral issues. 🤓
Machine learning models can analyze system logs, performance metrics, and sensor data to predict and identify potential peripheral failures before they become critical. 📉
Predictive maintenance based on AI insights can significantly reduce downtime and improve system reliability. 🛠️
The Future of Peripheral Integration in AI 🚀
As AI continues to evolve, so too will the landscape of peripheral integration. 🌌
We can expect several key trends: 👇
- Greater Standardization: Industry bodies will likely push for even more robust and widely adopted standards for AI peripheral communication, simplifying integration across diverse platforms. 🔗
- Self-Healing Systems: AI systems will become more adept at self-diagnosing and even self-correcting peripheral issues, reducing the need for human intervention. 🚑
- Modular and Swappable Hardware: The emphasis will be on highly modular hardware designs that allow for easy upgrades, replacements, and dynamic reconfigurations of AI systems. 🧩
- Integrated Edge AI: More peripherals will come with built-in AI capabilities, processing data locally before sending only relevant information to a central AI, reducing bandwidth and latency. 🚀
- Enhanced Security by Design: Security will be a core consideration from the initial design phase of both peripherals and AI systems, with advanced encryption and authentication mechanisms. 🔒
The goal is to create truly autonomous and resilient AI systems that can seamlessly adapt to changing environments and peripheral landscapes. 🎯
This future promises even more powerful and pervasive AI applications across all sectors. 🌍
Staying ahead of these trends will be vital for organizations leveraging AI. 📈
Infographics: Visualizing AI Peripheral Compatibility
Here’s an infographic summarizing the key aspects of AI peripheral integration. 🖼️
It highlights the challenges and solutions discussed. 📊
Conclusion 🎉
The AI integration imperative underscores the critical importance of advanced peripheral compatibility and robust troubleshooting in the age of artificial intelligence. 🌐
As AI systems become more complex and integral to our daily lives, the ability to seamlessly connect, manage, and maintain their physical interfaces will define their success. ✅
By understanding the challenges, adopting proactive strategies, and embracing advanced troubleshooting techniques, we can unlock the full potential of AI. 🔓
This ensures that our intelligent machines are not just smart, but also reliable, adaptable, and truly integrated into the world around us. 🌟
The journey of AI is one of continuous evolution, and peripheral integration remains a cornerstone of its progress. 📈
Let’s continue to build systems that are not just intelligent, but also incredibly well-connected. 🔗
“The future of AI is not about replacing humans, but about augmenting human capabilities.” – Fei-Fei Li
Further Reading: External Resources 📚
For those eager to delve deeper into the fascinating world of AI integration and peripheral technology, here are some highly recommended external resources: 👇
- IBM on AI Integration – A comprehensive overview of AI integration strategies and challenges from a leading industry expert. 💡
- Robotics.org on AI in Robotics – Explore how AI drives advancements in robotics, emphasizing the role of sensors and actuators. 🤖
- Intel’s Guide to AI at the Edge – Learn about the intricacies of edge AI devices and their integration with broader AI ecosystems. 🌐
- The Robot Operating System (ROS) – Discover how ROS provides a flexible framework for writing robot software, highlighting middleware solutions. 💻
- NIST on Standards in Technology – Understand the importance of standardization in technological development and integration, particularly relevant for peripherals. 📐
