Hey there, tech enthusiasts and everyday computer users!
Have you ever plugged in a new gadget, only to be met with a blank stare from your computer screen?
Or perhaps your trusty printer suddenly decided to go on strike after a system update?
If so, you’re not alone. Peripheral integration, while seemingly straightforward, can often be a complex dance between hardware and software,
especially with the ever-evolving landscape of modern operating systems.
Today, we’re diving deep into the ‘Software Secrets’ behind these advanced peripheral integration issues,
unraveling the mysteries, and arming you with the knowledge to troubleshoot like a pro.
Let’s get started!
Videos are added as random thoughts 💭 💭 💭…
The Perplexing World of Peripheral Integration
Modern operating systems, whether it’s Windows, macOS, or Linux, are designed to be versatile and support a vast array of peripheral devices.
From your mouse and keyboard to printers, scanners, external drives, and even specialized hardware, these devices extend the functionality of your computer.
However, the seamless integration we often expect isn’t always a given.
Several factors can throw a wrench into the works, leading to frustrating compatibility problems.
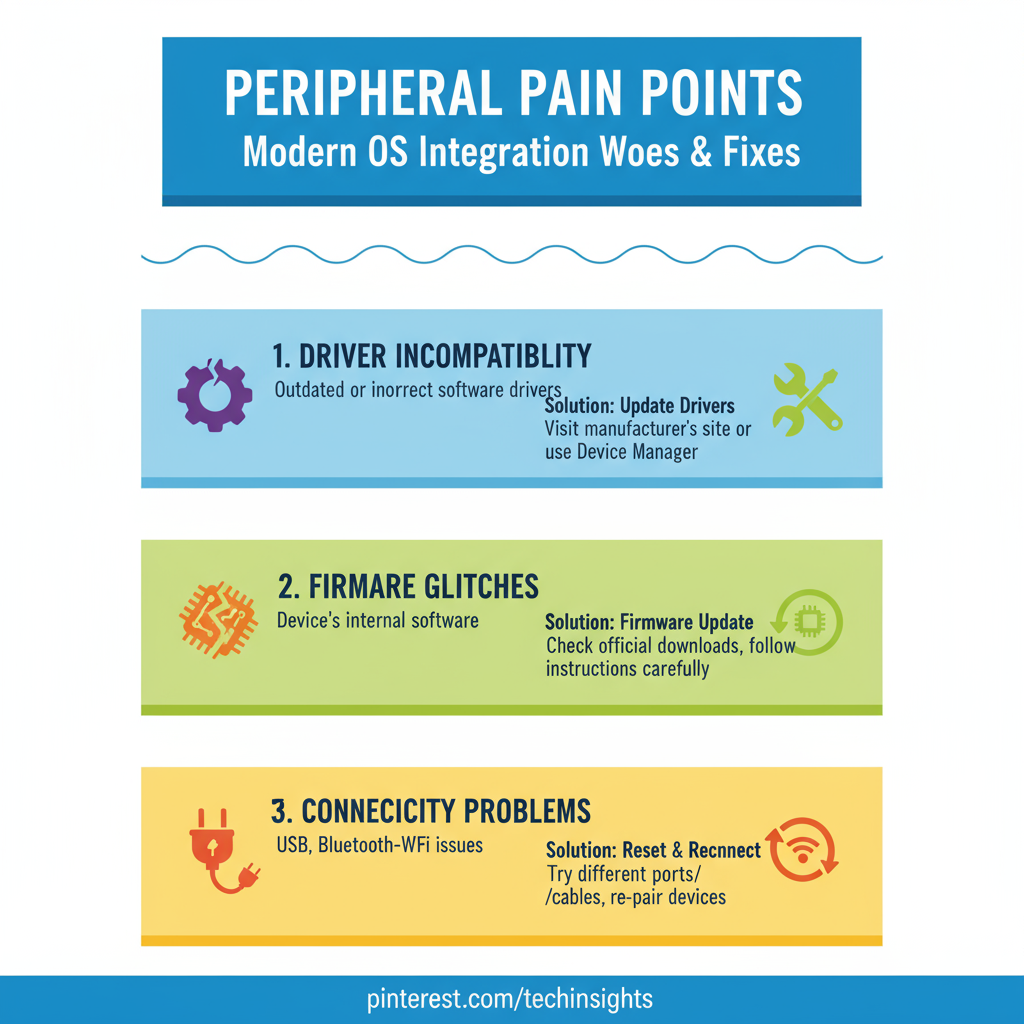
1. Driver Incompatibility: The Silent Saboteur
One of the most frequent culprits behind peripheral woes is driver incompatibility.
Think of drivers as the translators between your operating system and your hardware.
Each peripheral needs a specific set of instructions (a driver) to communicate effectively with the OS.
When these drivers are outdated, corrupted, or simply not designed for your current operating system version, your peripheral might as well be speaking a foreign language.
I’ve personally experienced this when upgrading my operating system.
My old, reliable printer, which worked flawlessly on the previous version, suddenly became a glorified paperweight.
A quick check revealed that the manufacturer hadn’t released updated drivers for the new OS.
It’s a common scenario, and it can be incredibly frustrating.
Solutions:
Update Drivers Regularly: This is your first line of defense.
Always check the peripheral manufacturer’s website for the latest drivers compatible with your operating system.
Many manufacturers release frequent updates to address bugs and improve compatibility.
Use Device Manager (Windows) or System Information (macOS/Linux):
These built-in tools can help you identify problematic devices and often provide options to update or reinstall drivers. Sometimes,
a simple driver reinstallation can resolve mysterious issues.
Compatibility Modes: For older peripherals, try running their drivers or associated software in compatibility mode.
This tricks the system into thinking it’s running an older OS version, which might just be enough to get things working.
Consider Virtualization: If you have a mission-critical peripheral that absolutely refuses to cooperate with your modern OS,
running a virtual machine with an older, compatible operating system might be a viable, albeit more complex, solution.
2. Firmware Glitches: The Deep-Seated Dilemma
Beyond drivers, peripherals also have their own internal software, known as firmware.
This is the low-level programming embedded directly into the device, controlling its basic functions.
Just like operating systems and drivers, firmware can have bugs or become outdated, leading to unexpected behavior or complete failure.
What’s more concerning is that unsigned or vulnerable firmware can even pose significant security risks [1].
Imagine a scenario where a seemingly innocuous USB drive could, through malicious firmware, compromise your entire system.
This isn’t science fiction; it’s a real threat that security researchers have highlighted.
It’s a reminder that the security of your peripherals is just as important as the security of your operating system.
Solutions:
Check for Firmware Updates: Periodically visit the manufacturer’s website for your peripherals to see if there are any firmware updates available.
These updates often fix bugs, improve performance, and enhance security.
Be Wary of Unsigned Firmware: While not always easy to detect, be cautious about using peripherals from unknown sources or those that have known vulnerabilities related to unsigned firmware.
Stick to reputable brands and ensure you’re downloading updates from official channels.
3. Connectivity Conundrums: The Tangled Web
Even with perfect drivers and updated firmware, connectivity issues can plague peripheral integration.
This can range from simple cable problems to complex network protocol conflicts.
Wireless peripherals, in particular, can be susceptible to interference, signal drops, or incorrect pairing.
I once spent an hour trying to figure out why my wireless mouse wasn’t responding, only to discover the USB receiver had come loose from its port.
Sometimes, the simplest solutions are the hardest to spot!
Solutions:
Basic Troubleshooting: Always start with the basics: check cables, try different USB ports, and ensure wireless devices are charged and properly paired.
A quick reset of the peripheral or even your computer can often resolve transient connectivity glitches.
Update Network Drivers and Firmware:
For network-dependent peripherals (like network printers or wireless adapters), ensure your network card drivers and router firmware are up-to-date.
Incompatible network protocols or outdated firmware can cause communication breakdowns.
Configure Network Settings: Sometimes, adjusting network settings like IP addresses, subnet masks, or even firewall rules can resolve connectivity issues.
Ensure that your network allows communication between your computer and the peripheral.
Perform Network Diagnostics: Operating systems offer built-in network diagnostic tools that can help pinpoint the source of connectivity problems.
Tools like `ping` or `traceroute` can be invaluable for diagnosing network communication.
4. Application Interoperability: When Software Collides
It’s not always about the peripheral itself; sometimes, the problem lies in how different applications interact with the peripheral or with each other.
Conflicting software components, incompatible data formats, or poorly designed integration can lead to unexpected behavior.
For example, I’ve seen instances where a specific photo editing software wouldn’t recognize my scanner, even though the scanner worked perfectly with other applications.
It turned out to be a conflict within the software’s own integration modules.
Solutions:
Use Integration Tools/Middleware: For complex setups, consider using integration tools or middleware that can act as a bridge between incompatible applications.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and data connectors are designed to facilitate seamless communication.
Standardize Data Formats: When working with multiple applications and peripherals, try to standardize data formats.
Using common formats like CSV or XML can prevent compatibility headaches and ensure smooth data exchange.
Keep Applications Updated: Just like operating systems and drivers, keeping your applications updated is crucial.
Software developers frequently release patches and updates that address interoperability issues and improve overall compatibility.
Consult Vendor Support: If you’re facing persistent application interoperability issues, don’t hesitate to reach out to the software vendor’s support.
They might have specific solutions, workarounds, or even patches to address the problem.
5. Security and Compliance Conflicts: The Unseen Barriers
In our increasingly security-conscious world, security software and compliance requirements can sometimes inadvertently create conflicts with peripherals.
Antivirus programs, firewalls, or strict corporate security policies might block legitimate peripheral functions, leading to integration problems.
I once had a client whose new biometric scanner wouldn’t work, and after hours of troubleshooting,
we discovered their corporate security software was flagging it as a potential threat.
A simple whitelist entry resolved the issue.
Solutions:
Review Security Policies: If you suspect security software is causing issues, review your security policies and configurations.
Ensure that legitimate applications and processes related to your peripherals are not being blocked.
Whitelist Applications/Devices: Configure your security software to whitelist trusted peripheral applications or even the devices themselves.
This tells the security software to allow them to operate without interference.
Stay Informed on Regulations: For businesses, staying up-to-date with security and compliance regulations is vital.
This ensures that your systems remain compliant while also allowing necessary peripherals to function.
Test Changes in a Controlled Environment:
Before deploying new security measures or making significant changes to your system, test them in a controlled environment.
This helps identify potential conflicts with peripherals before they impact your daily operations.
The Road Ahead: Towards Seamless Integration
As technology continues to advance, the complexity of peripheral integration is likely to grow.
However, by understanding the common pitfalls and adopting proactive troubleshooting strategies, you can navigate this landscape with confidence.
Remember, the goal is to create a harmonious ecosystem where your operating system and peripherals work together seamlessly, empowering you to achieve more.
So, the next time your printer throws a tantrum or your external hard drive plays hide-and-seek, take a deep breath, and remember these software secrets.
With a little patience and the right approach, you’ll be decoding those integration issues in no time!
References:
[1] Eclypsium. (2020, February 18). *Perilous Peripherals:
The Hidden Dangers Inside Windows & Linux Computers*. Retrieved from
/
