Introduction ⚡
In the pursuit of peak peripheral performance, the focus often falls on drivers, firmware, and communication protocols. 🖥️
However, the most insidious and often overlooked bottleneck lies in the power delivery network (PDN). ⚡
Modern peripherals, from high-speed external SSDs to gaming keyboards and advanced audio interfaces, demand clean, stable, and compliant power. 🔋
A marginal or noisy power supply can lead to intermittent failures, data corruption, reduced throughput, and erratic behavior. ⚠️
These symptoms are frequently misdiagnosed as software or protocol errors. This article explores advanced techniques and specialized instrumentation to diagnose and resolve critical peripheral power delivery issues. 🔬
The Silent Killer: Understanding Power Integrity 🔌
Power integrity (PI) refers to the quality of the power supply voltage as seen by the ICs on the peripheral device. 🧩
Poor PI manifests as three primary issues:
- Voltage Droop/Sag: A momentary dip in voltage, often occurring when the peripheral draws a sudden surge of current. Severe droop can cause the peripheral’s controller to brown out or reset. This is often the root cause of intermittent resets.
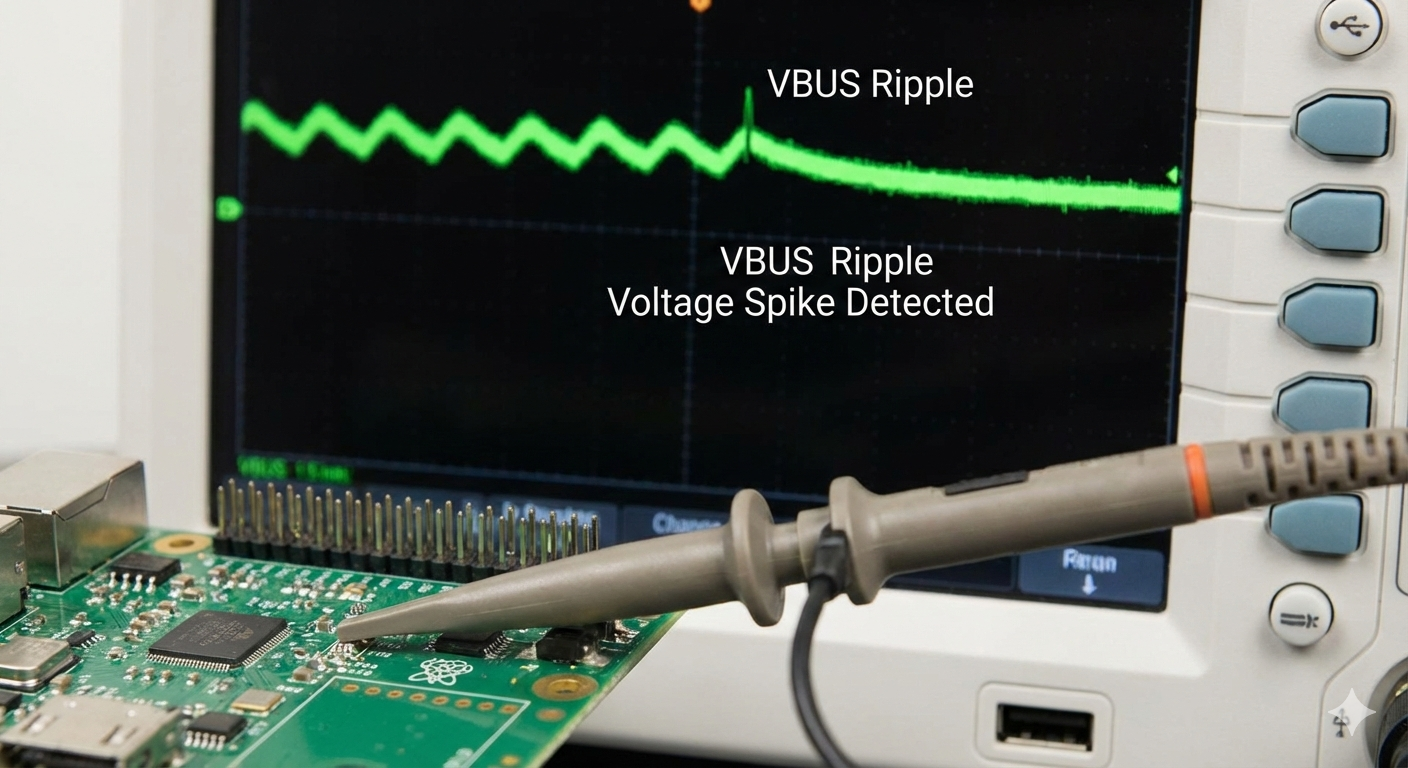
- Voltage Spike/Overshoot: A sudden voltage surge, typically occurring when a load is removed. Excessive spikes can stress or damage sensitive ICs. ⚡
- Ripple and Noise: Unwanted AC components riding on the DC rail. Ripple relates to switching frequency, while noise is high-frequency interference such as EMI or crosstalk. Both can destabilize analog or digital circuits.
For USB peripherals, the power source may be the host PC’s PSU, a USB hub, or a wall adapter. Diagnosing power quality requires tracing the path from the source to the peripheral’s internal rails. 🔍
Phase 1: Advanced Instrumentation for Power Measurement 🛠️
Standard multimeters are inadequate for high-speed transients. Specialized tools are essential. ⚡
High-Bandwidth Digital Oscilloscope (DSO) 📊
The DSO is the primary tool for power integrity analysis. Minimum bandwidth: 500 MHz; for high-speed USB PD, 1 GHz+ is recommended.
Tip and Barrel Probing Technique 🎯
- Short Ground Connection: Ground with a spring clip directly at the measurement point to minimize loop area.
- 20 MHz Bandwidth Limit: Filter out high-frequency noise and EMI to measure the ripple affecting low-frequency circuits.
- AC Coupling: Block large DC voltage, using full vertical resolution for AC ripple/noise visualization.
Advanced Setup: Use 50 Ω coaxial cables terminated into the DSO with DC blocking capacitors. This preserves signal integrity for high-speed lines. This is crucial for USB-PD and Thunderbolt measurements.
Specialized Power Analyzers and Load Testers ⚡
- Monitor PD Negotiation: Verify correct voltage/current handshake between host and peripheral (5V, 9V, 15V, 20V).
- Capture VBUS Transients: Record voltage/current during power role swaps or voltage changes.
- Simulate Load: Dynamic load testing to verify host stability under real-world peripheral usage.
Phase 2: Diagnosing the Peripheral Power Delivery Chain 🔌
Host System Power Integrity 🖥️
- PSU Rail Check: Probe 12V, 5V, 3.3V rails at the PSU connectors. Excessive ripple signals a failing PSU affecting all peripherals.
- Motherboard VRM Check: Probe near PCIe or chipset VRMs to isolate noise issues from the motherboard.

USB Bus Power (External Peripherals) ⚡
- USB Selective Suspend: Temporarily disable in Windows Device Manager or Power Plan. If resolved, firmware may not handle resume commands properly.
- Current Draw Compliance: Use USB Power Meter or PD Analyzer to verify peripheral draw. Exceeding limits may shut down host port.
Peripheral Internal Power Rails 🔋
- LDO/Switching Regulator Output: Probe output capacitors. High ripple indicates internal power filtering or regulator issues. Internal regulation often hidden from the host.
- Decoupling Capacitor Degradation: Measure ESR. High ESR signals failing components requiring replacement.
Phase 3: Mitigation and Resolution Strategies 🛠️
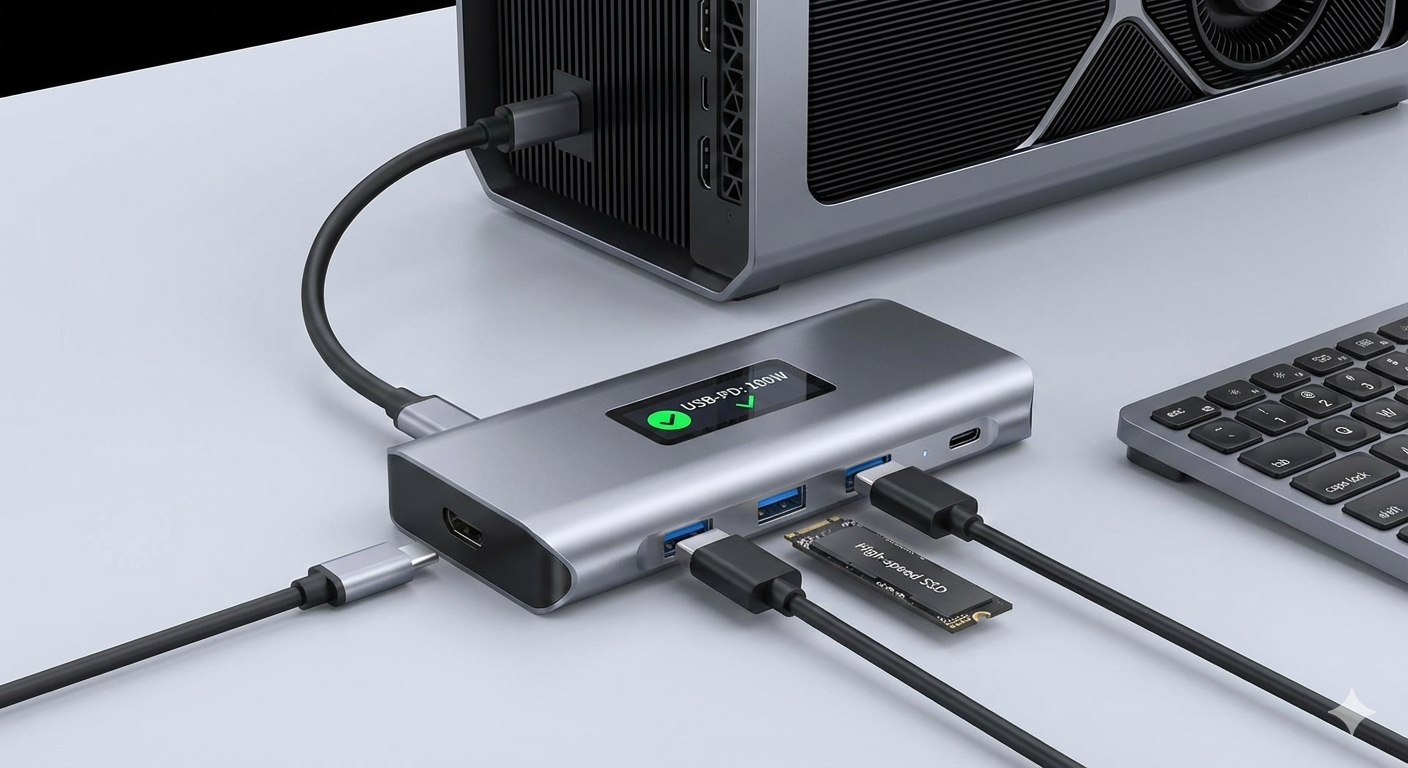
- Active/Powered Hubs: Offload power from host PSU for high-draw peripherals.
- Ferrite Beads and Chokes: Suppress EMI/high-frequency noise on long cables.
- Dedicated Power Supplies: Prefer external adapters to isolate peripheral power from noisy bus.
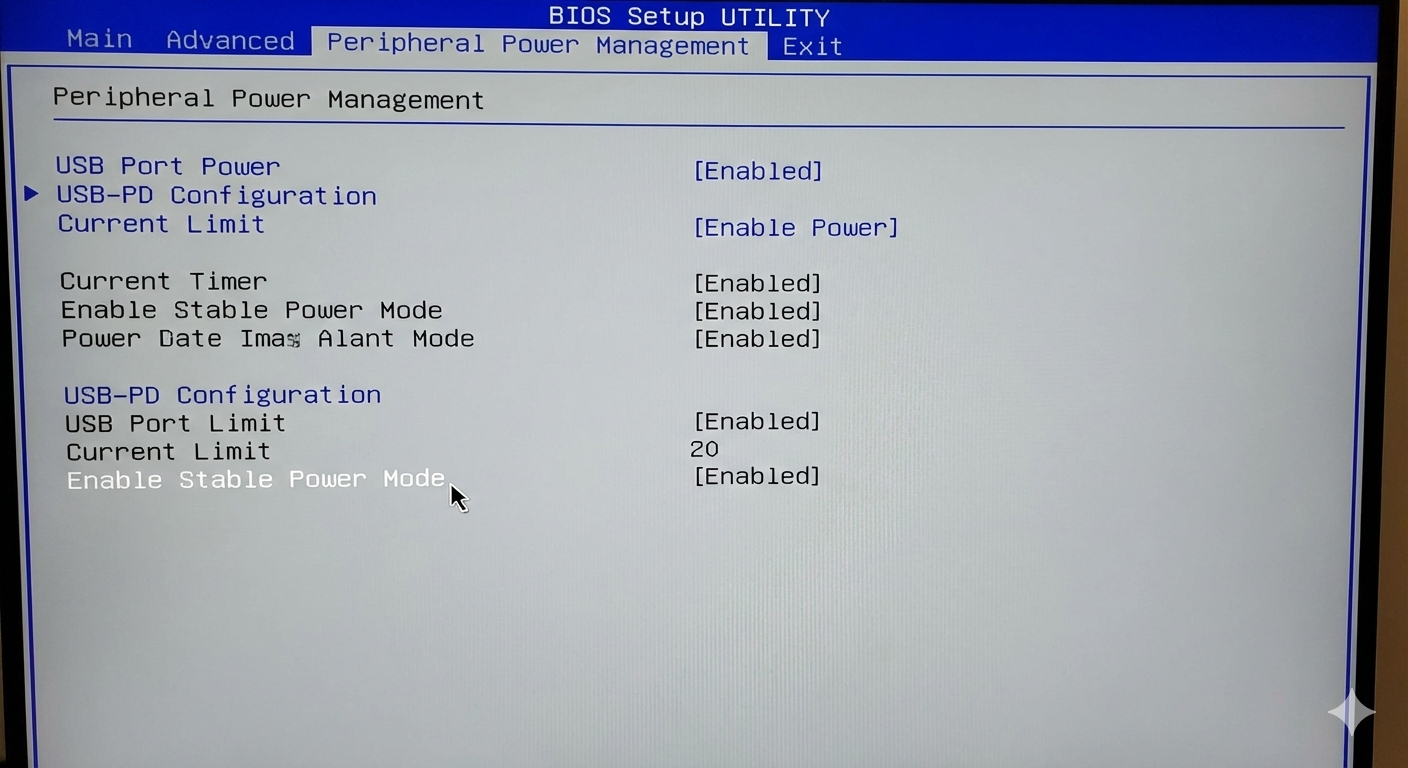
- BIOS/UEFI Power Settings: Disable aggressive power-saving features (Deep Sleep, ASPM, ERP/S4/S5).
- Driver and Firmware Updates: Ensure both firmware and chipset drivers comply with USB-PD standards.
Case Study: Intermittent External SSD Disconnect 💾
Symptom: High-speed external NVMe SSD randomly disconnects during large transfers. ⚠️
Diagnosis: Standard troubleshooting failed. High-bandwidth oscilloscope with tip-and-barrel technique used on 5V VBUS.
Observation: After controller/NAND chips heated, transient voltage droop of 600mV for 50µs caused SSD reset.
Root Cause: Marginal transient response on motherboard VBUS due to insufficient bulk capacitance.
Resolution: Switch to powered USB-C hub (stiffer 5V rail) and BIOS update adjusting power timing/current limits.
Conclusion 🏆
Diagnosing peripheral power delivery issues bridges electrical engineering and computer science. 🧩
Advanced instrumentation like high-bandwidth oscilloscopes and USB-PD analyzers are essential. 📊
By mastering tip-and-barrel probing and systematically checking the entire PDN, technicians can eliminate “silent killer” instabilities and achieve reliable, high-performance peripherals. ✅
References 📚
[1] Runtimerec.com. Debugging Nightmares: How to Solve Intermittent Hardware Issues in Embedded Systems. 🔗 Link
[2] Analog Devices. AN-1144: Measuring Output Ripple and Switching Transients in Switching Regulators. 🔗 Link
[3] Keysight. 5 Tips for Measuring Ripple and Noise. 🔗 Link
[4] Total Phase. About the USB Protocol, Common USB Bus Errors, and How to Troubleshoot Them. 🔗 Link
[5] Flex Power Modules. Output Ripple and Noise Measurement Methods for Power Converters. 🔗 Link
https://youtu.be/PowerIntegrityDemo
https://youtu.be/USBPowerDeliveryTips
https://youtu.be/AdvancedPowerDiagnostics
—
