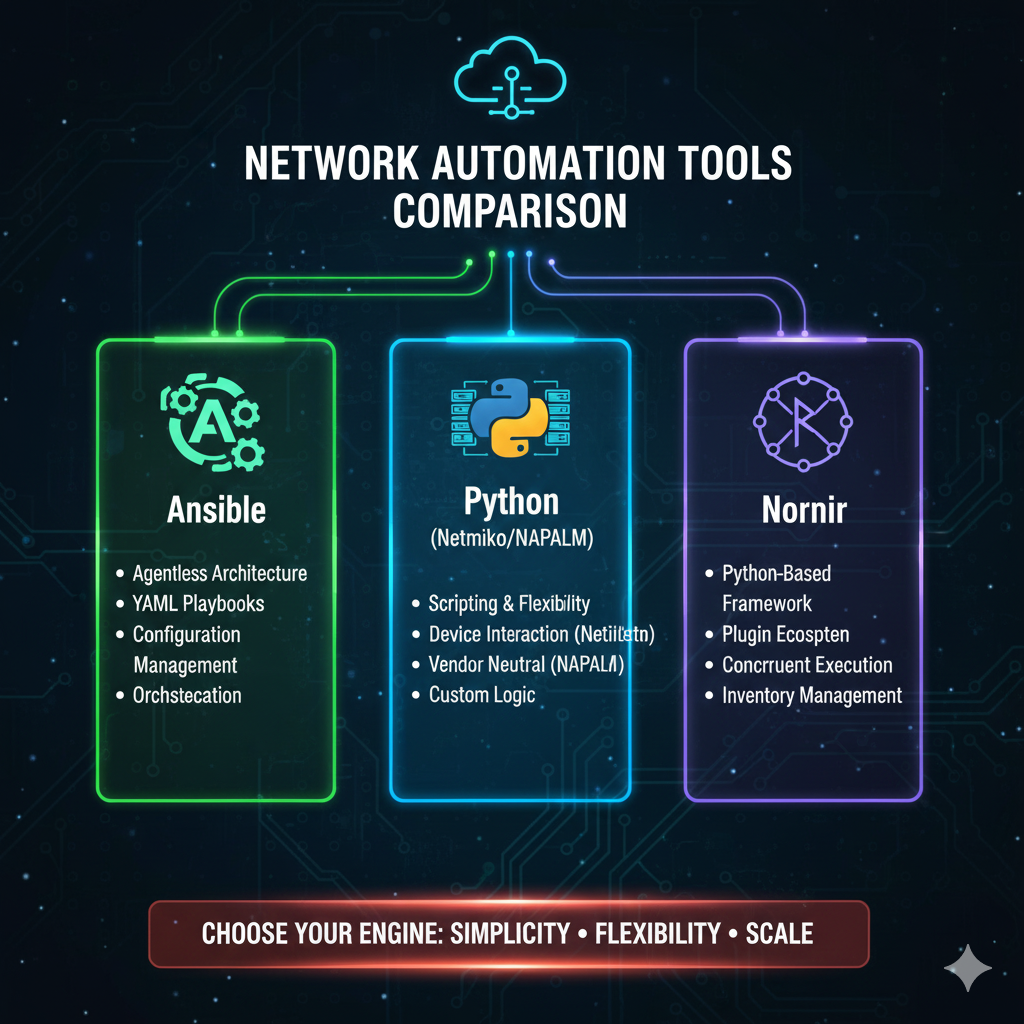
Network Automation Tools Comparison: Choosing the Right Engine for Your Infrastructure 🤓
Network automation has moved from a niche skill to a core competency for modern network engineers.
The sheer scale and complexity of today’s networks make manual configuration and troubleshooting unsustainable.
Automation not only reduces human error but also enables faster deployments, better compliance, and greater agility.
However, the landscape of tools is diverse, ranging from simple Python libraries to full-fledged configuration management frameworks.
Choosing the right tool—or combination of tools—is the first critical step toward a successful automation strategy [1].
This guide provides a detailed comparison of the most popular and powerful network automation tools available today.
The Declarative Powerhouse: Ansible
Ansible, an open-source automation engine, is arguably the most popular tool for network configuration management.
Its agentless architecture and human-readable YAML syntax make it an excellent entry point for network engineers.
Agentless and Simple
Ansible’s primary advantage is its simplicity.
It manages network devices over standard protocols like SSH, eliminating the need to install a client or agent on the target device.
YAML Playbooks
Automation tasks are defined in YAML-based playbooks, which are easy to read and understand, even for non-developers.
Idempotency
Ansible is designed to be idempotent, meaning you can run the same playbook multiple times, and it will only make changes if the device’s state does not match the desired state.
Modules
It leverages a vast collection of modules, including specific modules for major network vendors (Cisco, Juniper, Arista, etc.), abstracting away the low-level CLI commands.
Ansible excels in configuration management, compliance checks, and orchestration across a large, heterogeneous network infrastructure.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0h59gY0t4sI
The Imperative Foundation: Python and Libraries
Python is the foundational language for network automation.
While Ansible provides a high-level, declarative approach, Python, combined with specialized libraries, offers granular, imperative control over network devices.
Netmiko: The SSH Swiss Army Knife
Netmiko is a Python library built on top of Paramiko (an SSH library) that simplifies the process of sending and receiving CLI commands to network devices.
CLI Interaction
It handles the complexities of SSH connections, including device prompts, paging, and error handling, allowing engineers to script the exact CLI commands they would type manually.
Vendor Support
Netmiko supports a massive number of network vendors and platforms, making it highly versatile for multi-vendor environments.
NAPALM: The Abstraction Layer
Network Automation and Programmability Abstraction Layer with Multivendor support (NAPALM) is a Python library that provides a unified API to interact with different network operating systems.
Standardized Data Models
Instead of sending raw CLI commands, NAPALM allows you to retrieve and manipulate network data (e.g., interfaces, BGP neighbors, facts) using standardized data structures, regardless of the vendor.
Configuration Management
It supports operations like merge, replace, and rollback for configuration changes, providing a safer, more structured approach than raw CLI scripting.
Python with Netmiko and NAPALM is the choice for engineers who need maximum flexibility, complex logic, and deep, low-level control over device interactions.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v5g9t31343E
The Python Orchestrator: Nornir
Nornir is a pure Python automation framework that acts as an inventory management and task execution engine.
It is designed to bridge the gap between the simplicity of Ansible and the power of Python scripting [3].
Inventory and Multi-Threading
Nornir’s strength lies in its ability to manage inventory and execute tasks in parallel using Python’s multi-threading capabilities.
Pure Python
All configuration and logic are written in Python, allowing for complex, custom automation workflows that are difficult to achieve with YAML-based tools.
Plugin Ecosystem
It uses a plugin system to integrate with other tools, such as Netmiko and NAPALM, allowing you to leverage their capabilities within the Nornir framework.
Structured Results
Nornir returns structured, easily parsable results, making it ideal for large-scale data gathering and validation tasks.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Qh8j0v0_t0
Comparison of Network Automation Tools
The best tool is often the one that fits the specific task and the team’s skill set.
A combination of these tools is common in advanced automation environments.
| Tool | Primary Language | Architecture | Approach | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ansible | YAML (Python core) | Agentless (SSH) | Declarative | Configuration management, compliance, orchestration |
| Python (Netmiko) | Python | Agentless (SSH) | Imperative | Low-level CLI scripting, simple data gathering |
| Python (NAPALM) | Python | Agentless (SSH/API) | Abstraction/Imperative | Multi-vendor configuration, standardized data retrieval |
| Nornir | Python | Agentless (SSH) | Imperative/Orchestration | Large-scale parallel execution, complex custom workflows |
Conclusion
The choice between these tools is often a choice between declarative simplicity (Ansible) and imperative control (Python/Nornir).
For most organizations starting their automation journey, Ansible provides the quickest path to value for configuration tasks.
However, as automation needs become more complex—involving custom logic, complex data manipulation, or high-speed parallel execution—the power of Python with libraries like Netmiko, NAPALM, and the Nornir framework becomes indispensable [2].
The most effective network automation strategy involves a hybrid approach, leveraging the strengths of each tool to build a robust, scalable, and resilient infrastructure.
The most effective network automation strategy involves a hybrid approach, leveraging the strengths of each tool to build a robust, scalable, and resilient infrastructure.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7hK94y1qf7I
References
[1] Automation tools: Paramiko, Netmiko, NAPALM, Ansible – APNIC Blog
[2] Ansible vs. Python + Netmiko (or Nornir) – Reddit
[3] Paramiko, Netmiko, NAPALM or Nornir? – IP Space
[4] 15 Network Automation Tools in 2025 – InvGate Blog
[5] Network Automation Tools Comparison – Rayka Co
YouTube Videos
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0h59gY0t4sI
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v5g9t31343E
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Qh8j0v0_t0
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7hK94y1qf7I
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k9h9g-69w0k
