Edge Computing Network Architecture: Bringing Processing Power Closer to the Data Source 🤓
For years, the centralized cloud model reigned supreme, with massive data centers handling the bulk of the world’s computing.
However, the explosive growth of the Internet of Things (IoT), the demand for real-time processing, and the rollout of 5G networks have exposed the limitations of this model, particularly concerning latency.
Edge Computing is the paradigm shift that addresses this challenge by moving computation and data storage closer to the location where the data is generated, or the “edge” of the network [1].
This distributed architecture is essential for applications that require near-instantaneous response times.
The Core Concept: Decentralization
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm.
Instead of sending all raw data from devices (the edge) to a distant central cloud for processing, the processing power is strategically placed at various points between the data source and the cloud.
Why the Edge?
The primary drivers for adopting an edge architecture are:
Low Latency
Critical for applications like autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and industrial automation, where a delay of even a few milliseconds can be catastrophic.
Bandwidth Optimization
Processing data locally reduces the volume of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud, saving bandwidth and cost.
Data Sovereignty and Security
Keeping sensitive data local can help meet regulatory compliance requirements and reduce the attack surface.
Edge computing is not a replacement for the cloud; it is a complementary architecture that extends the cloud’s capabilities to the physical world.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0h59gY0t4sI
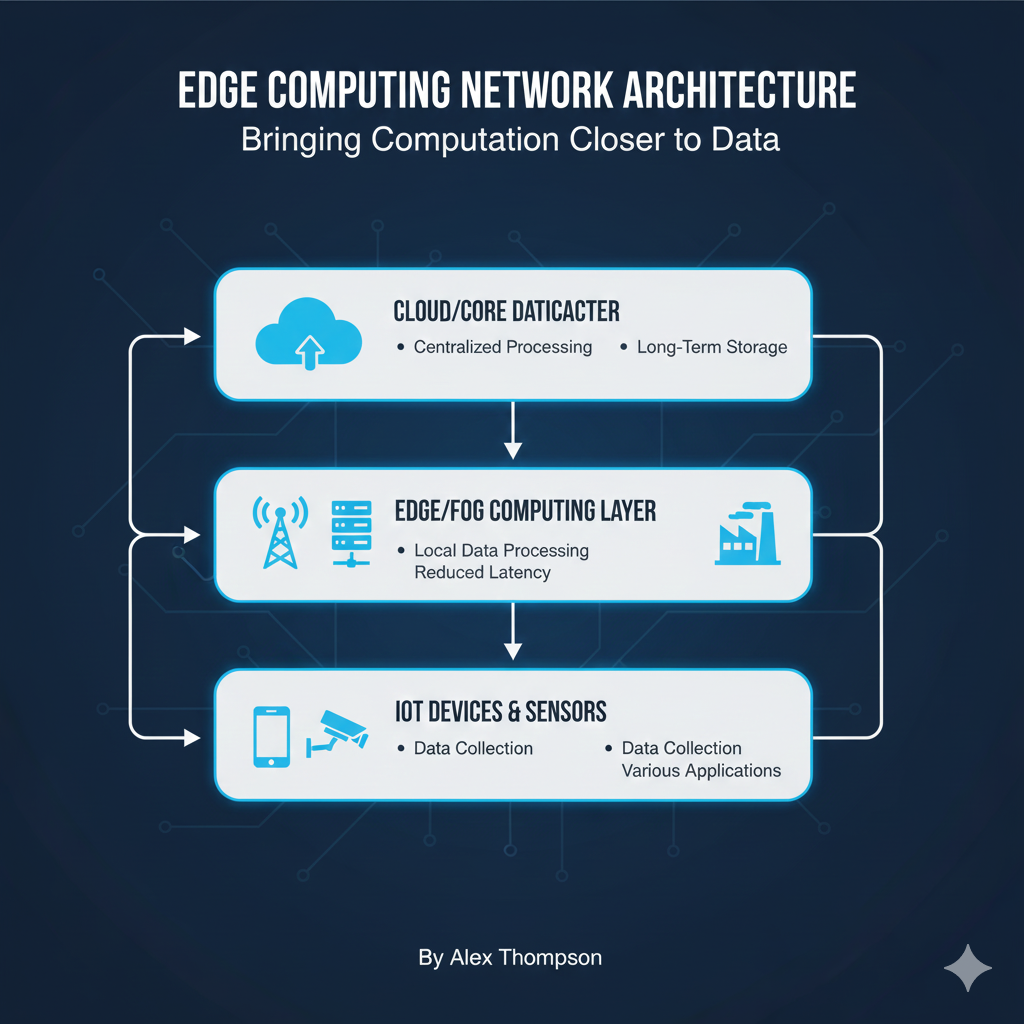
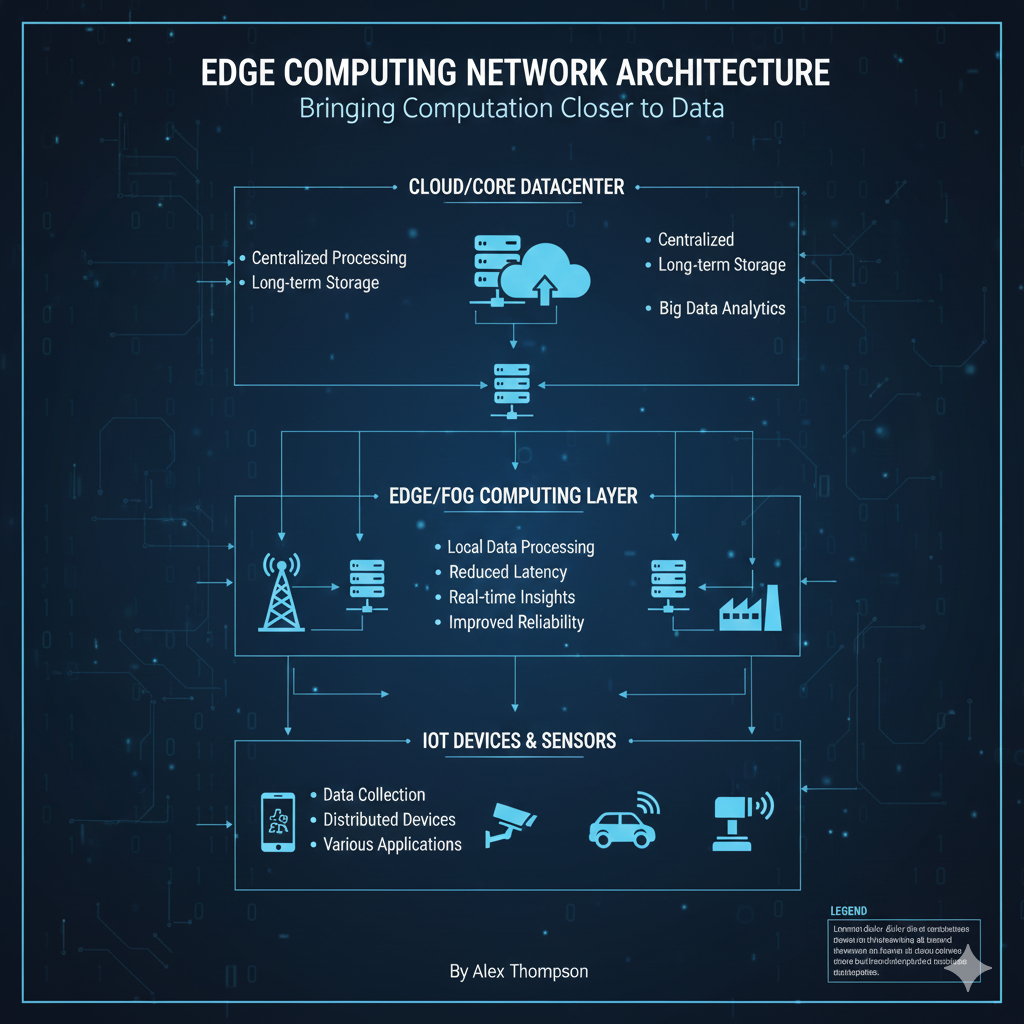
Key Components of the Edge Architecture
The edge network architecture is typically divided into three main layers, working together to manage the flow of data.
1. The Device Edge (The Source)
This layer consists of the physical devices that generate the data.
Edge Devices
Sensors, IoT devices, smart cameras, industrial machinery, and mobile phones.
These devices often have limited processing power and are primarily focused on data collection.
Data Generation
The sheer volume and velocity of data generated at this layer necessitate local processing.
2. The Near Edge (The Gateway/Server)
This is the intermediate layer where the initial, critical processing occurs.
Edge Gateways
These devices aggregate data from multiple edge devices, perform protocol translation, and execute initial filtering or pre-processing.
They act as the bridge between the device edge and the rest of the network.
Edge Servers/Micro Data Centers
These are small-scale computing and storage facilities strategically placed closer to the device edge—in a factory floor, a retail store, or a cell tower.
They run edge-native applications and perform complex analytics that require low latency [2].
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v5g9t31343E
3. The Far Edge (The Cloud/Core)
This layer represents the traditional centralized data center or public cloud.
Centralized Processing
The cloud handles long-term storage, large-scale batch analytics, machine learning model training, and global management of the entire edge infrastructure.
Orchestration
The cloud provides the control plane for deploying, managing, and updating applications running on the distributed edge servers.
The network connecting these layers must be robust, often leveraging 5G for high-speed, low-latency connectivity between the device edge and the near edge [3].
Edge Deployment Models
Edge computing is not a one-size-fits-all solution.
Different use cases require different deployment models.
| Deployment Model | Location of Edge Server | Primary Use Case | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Device Edge | Directly on the device | Ultra-low latency, real-time control | Autonomous vehicle sensor processing |
| On-Premises Edge | Local data center, factory floor, retail store | Local data processing, compliance | Industrial IoT, smart retail analytics |
| Service Provider Edge | Cell tower, central office (MEC) | 5G applications, network optimization | Mobile gaming, augmented reality |
| Cloud Edge | Cloud provider’s regional data center | Content delivery, regional data aggregation | Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) |
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Qh8j0v0_t0
Edge Computing and Network Security
The distributed nature of edge computing significantly complicates network security.
The traditional perimeter is completely dissolved, making the Zero Trust model a necessity.
Increased Attack Surface
Every edge device and server is a potential entry point.
Zero Trust Mandate
Security must be applied at the device level, with continuous authentication and micro-segmentation to prevent lateral movement across the distributed network [4].
Remote Management
Edge devices are often deployed in remote, unsecured locations, requiring robust, secure remote management and patching capabilities.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7hK94y1qf7I
Conclusion
Edge computing network architecture is the next evolution of distributed computing, driven by the need for speed and the explosion of data from IoT devices.
By strategically placing processing power closer to the data source, organizations can unlock new capabilities in real-time automation, AI, and immersive experiences.
This shift requires a fundamental redesign of the network, moving away from centralized models and embracing a secure, distributed, and highly automated infrastructure.
Mastering the edge architecture is key to leveraging the full potential of 5G and the next generation of intelligent applications [5].
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k9h9g-69w0k
References
[1] The Complete Guide to Edge Computing Architecture – Mirantis
[2] What is Edge Architecture? – GeeksforGeeks
[3] What is Edge Computing – Distributed architecture – Cisco
[4] What Is Edge Computing? Definition, Benefits &… – Scale Computing
[5] Edge Computing Architecture Guide – ZPE Systems
YouTube Videos
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0h59gY0t4sI
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v5g9t31343E
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Qh8j0v0_t0
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7hK94y1qf7I
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k9h9g-69w0k
